Hair Loss Treatments
-
Content written by Andrew Proulx, MD | Reviewed by EnhanceMyself Medical Team | Last updated 6/12/2023
- Overview
Overview
What is alopecia?
Hair loss, also called alopecia, refers to the loss of hair from any part of the human body. While losing a certain amount of hair during the course of each day is normal, up to 50% of people aged 50 years or older experience hair loss to the point of thinning or balding.
Normal hair growth cycle
Throughout our lives the body sheds, on average, 100 to 150 hairs per-day during its natural growth-cycle, which is made up of three phases:
- Anagen: The active growth stage for hair follicles. It lasts 2 to 6 years for scalp hair and typically only several months for other body hair. This length of time is genetically determined but can also be impacted by external factors such as stress and illness. At the end of the anagenic phase the follicle then enters the catagen phase.
- Catagen: A short transitional phase lasting 2-3 weeks. The follicles shrink to about 1/6 of their normal length and a new hair forms underneath the existing one before the old hair falls out.
- Telogen: The resting phase of the follicle during which the old hair is finally shed from the body.
Causes of hair loss
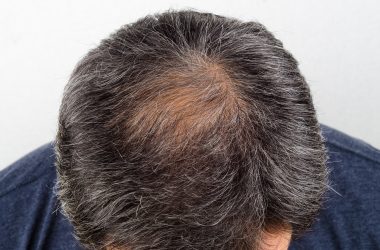 Hair loss can be caused by a number of factors, including:
Hair loss can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Hereditary hair loss (androgenic alopecia): This is a common form of hair loss in men, and sometimes in women. This is hereditary and can be inherited from one or both parents. While this type of hair loss is often referred to as male pattern baldness, it can occur in both males and females. Pattern hair loss is a more accurate term that can be applied to both men and women.
- Health problems: Diseases that can cause hair loss include thyroid problems, scalp infections and lupus. Treatments for cancer such as radiation and chemotherapy can contribute to hair loss as well.
- Stress: Physical stress can cause hair loss. Stressors can surgical trauma, high fever and chronic illness.
- Hair Damage: Repeated hair damage from heat, chemicals or traction can cause breakage which leads to hair loss. Hair loss resulting from traction from braiding or putting hair in ponytails is called traction alopecia.
- Aging: As we grow older our hair naturally gets thinner and more brittle causing the body to have an increased amount of hair loss.
Being aware of the factors that contribute to hair loss can help you properly treat it. Certain factors such as diet, stress and disease can be easily identified and addressed, while others, such as pattern hair loss, may require more intensive treatment.
Non-surgical treatments
For those experiencing hair loss, there are several non-surgical options:
- Propecia (Finasteride): This is a steroid that blocks the body’s conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is the primary cause of pattern hair loss. By blocking the body’s production of DHT, research has shown it stops the progression of hair loss in close to 90% of those that use it. It is effective in stopping hair loss at the hairline. It is important to note that Propecia is only effective for as long as it is taken; hair loss restarts within 12 months after treatment is ended.
- Rogaine (Minoxidil): Rogaine is another recommended treatment for pattern hair loss. Rogaine is a vasodilator that is primarily effective in stopping and regrowing hair on the crown of the head. Like Propecia, Rogaine is only effective as long as it is used. Rogaine is available in varying strengths for men and women.
- Corticosteroids: While corticosteroids such as Dutasteride (Avodart) and Ketoconazole (Nizoral/Sebizole) have been shown to treat hair loss, they are not yet FDA approved for administration as hair loss treatments. Avodart is used to reduce prostate growth, while ketoconazole is used to treat fungal infections.
Surgical hair loss options
There are two primary hair transplant surgery options to consider: follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE). .
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) procedure: A strip of hair-bearing skin is taken from the back or side of the head. The hair follicles are then taken from the strip and transplanted into the desired areas. This procedure may involve minor pain. Stitches are required. The donor area takes about 2-3 weeks to heal, while the recipient area heals in 14 days.
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) procedure: Hairs are removed individually from the donor area using a special punch tool and then transplanted into the desired areas. This procedure is usually painless and does not require stitches. The donor area takes about 7 days to heal and the recipient area heals in 10-14 days.
Additional treatments
If you aren’t interested in topical or surgical hair-loss treatments, there are some other alternative options available.
- Low-level laser therapy (LLLT): While research on LLLT has shown conflicting results, some patients have seen improvement in hair density and diameter.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): A non-surgical treatment that utilizes the stem cells and growth factors from the patient’s own blood to trigger the growth of hair from resting or miniaturized hair follicles. When examining the effects of PRP in comparison to minoxidil, finasteride, and adult stem cell-based therapy, it was observed that 84% of all studies reported a favorable outcome with PRP. Out of these, 50% indicated a statistically significant improvement, while 34% noted enhancements in both hair density and hair thickness.
- Cosmetic Aids: Tinted powders, lotions and sprays can help camouflage hair loss by covering thinning spots on the scalp. Wigs, hair pieces, and hair extensions can also help to disguise hair loss.
Cost of hair loss treatments
The cost of hair loss treatments will vary greatly depending on the type of treatment and the extent of hair loss.
- Non-surgical treatments: On average patients spend between $30-$45 for a 3 month supply of Minoxidil.
- Hair transplant surgery: The cost of hair transplants varies, but usually ranges from $6,000 to $15,000. FUT is usually less expensive than FUE.
- Additional treatments: The cost of PRP and laser therapy for hair loss typically ranges from $1,500 to $3,500. The cost for cosmetic aids such as wigs can range from $99 to $500.
EnhanceMyself.com relies on sources such as professional medical organizations, government agencies, academic institutions, and peer-reviewed scientific journals to write it’s articles. Learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate, in-depth, and unbiased by reading our editorial guidelines.
*Medical Disclaimer: This website does not provide medical advice. Read more.

